GENERAL INTRODUCTION TO GENETIC
General information about DNA testing
Glossary
What is genetic?
- General definition : the study of an individual DNA in order to identify genetic differences responsible for the expression of certains traits (color coat, size,..) or particular diseases and abnormalities.

- Genetic testing is used in many areas of human and animal medicine.
- It can be done thanks to blood or saliva analysis.
What is not genetic?
- Genetics can influence a wide range of traits and characteristics , including physical attributes such as height, eye color, and hair texture, as well as predisposition to certain diseases or conditions. Some traits that are strongly linked to genetics include:
- Inherited disorders: These are conditions caused by mutations in specific genes that are passed down from parents to offspring
- Physical traits: Certain physical characteristics such as eye color, hair color and texture, height, and body shape are largely determined by genetics.
- Behavioral traits: Some behaviors such as temperament have a genetic basis.
- On the other hand, many traits and characteristics are not linked to genetics, and are instead influenced by environmental factors such as: diet, exercise, individual experiences, education, trauma, and social interactions can have a profound impact on an individual’s development and behavior.
Genetic and breeds
- The existence of breeds as we know them today are direclty link with genetic. Indeed, a dog breed is a particular strain of dog that was purposefully selected and bred by humans to perform specific task based on their physical traits and behavior.
- Starting from the original dog people have selected dogs for centuries based on their unques abilities building breeds generation through generation. We have more than 450 breeds recognized in the world today.
- All breeds have their own unique characteristics and abilities, presenting distinct traits in their looks and minds :
- Physical : body size and shape, tail phenotype, coat colour, skull shape, fur type,…
- Behavioral : companion, guarding, herding,…(hunting?)
- Personality : hyper-social behavior, boldness, and aggression.

Basic concepts of genetic: DNA
- Genetic consist in analyzing the animal DNA that contains the code for building the organism.
- What DNA looks like:

- Two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix
- Sequence of four chemical bases : A, C, G and T called nucleotide
• Pair with each other: A with T, C with G - Just like letters, they come together to form words and sentences
- In genetic the sentence resulting from the combination of letters is called a gene
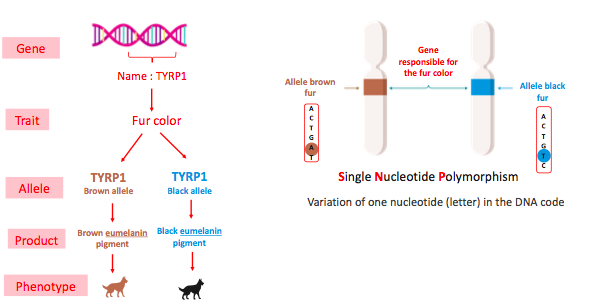
Basic concepts of genetic : GENE
• The gene is a portion of DNA that determines a certain trait (ex : coat color)

19,000 genes in dogs
Basic concepts of genetic : Allele
- Gene : portion of DNA that determines a certain trait, the different versions of a gene are called alleles.
- Allele:
- Specific form of a gene
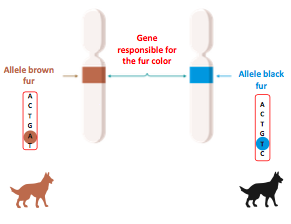
- 2 variants possible
-
differ by one nucleotide (letter)
responsible for the variations in the trait expression
- Specific form of a gene
DNA and gene create the animal Genotype…
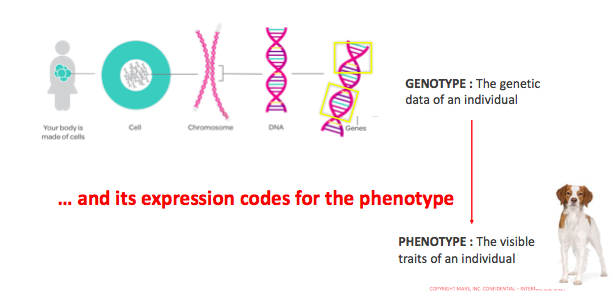
Link genotype – phenotype example :
Link genotype – phenotype example :
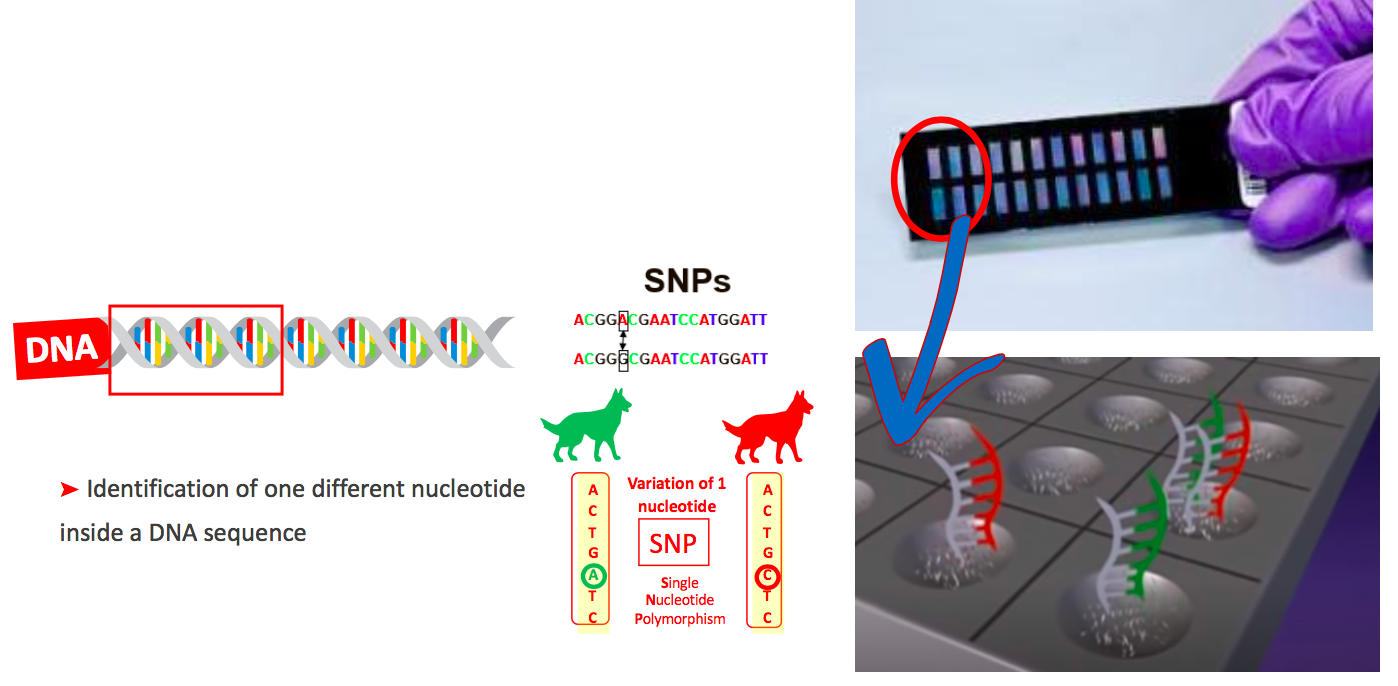
- This variation of nucleotide (SNP) can affect the gene function & trigger :

-
- Differences in appearance à Coat colour
- Hair size
- Body size
- Differences in appearance à Coat colour
-
 Differences in disease development
Differences in disease development
- Healthy animal
- Sick animal
Nothing : some gene variation does not have any impact on the dog appearance or health
6,000,000 SNPs in Dogs among 2,400,000,000 base pairs.
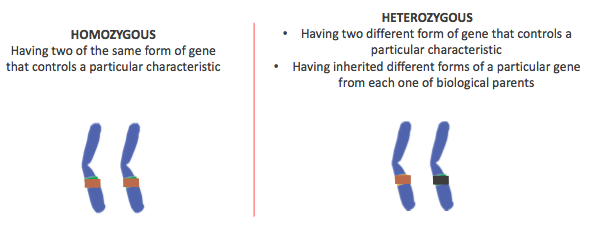
Basic concepts of genetic :
allele Homozygus VS Heterozygous
2 allèles of the same gene can be identical or different
Basic concepts of genetic : allele Dominant VS Recessive
There is two types of allele:

Basic concepts of genetic : heredity
- The genes are encoding for the animal phenotype

- Each person is born with two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent
Basic concepts of genetic :
- Gene pool : all of the genes in all of the individuals in a breeding population. More precisely, it is the collective genotype of a population.
- Gene flow : the transference of genes from one population to another, usually as a result of migration. The loss or addition of individuals can easily change the gene pool frequencies of both the recipient and donor populations–that is, they can evolve.
Basic concepts of genetic :
- Genetic diversity : The greater the number of alleles that are available at each gene pair (called genetic polymorphism), the greater the genetic diversity of the breed. If there is no breed diversity in a gene pair, but the particular homozygous gene that is present is not detrimental, there is no negative effect on breed health.
- Inbreeding : Inbreeding occurs when puppies are produced from two related dogs, i.e. dogs with relatives in common. High levels of inbreeding can affect the health of these puppies.
UAGE OF DNA TEST TO IMPROVE HEALTH
More scientific section targeting health professionnals
Human and dogs have a very long history
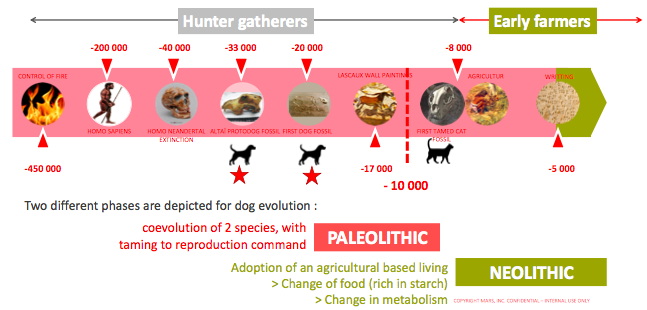
Recent history: huge variability of modern dogs
 Intensive Breeding started 4 centuries ago
Intensive Breeding started 4 centuries ago- Real Breed Standard appears in the 16 century
- First world canine exhibition (conformation) :
- Manchester 1859
- London 1862
- Paris 1863
350
BREEDS+ OVER THE PAST 400 YEARS

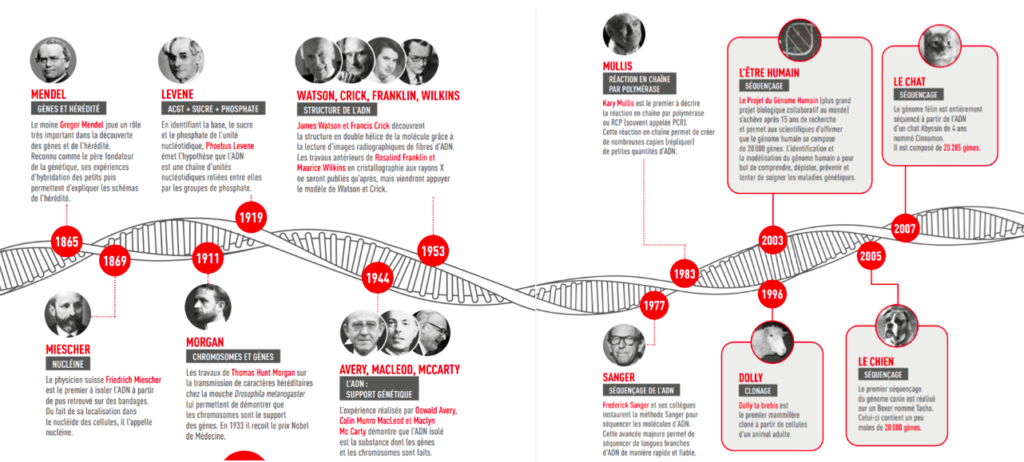
History of DNA testing
DNA testing and animal reproduction
The usage of genetic test allows to identify certain genetic mutations that are associated with the expression of various treats or disease in dogs. It allow to trace where those mutations came from.
Having this knowledge before mating dogs or cats together is key to rightly predict the appearance of the offspring and be sure to eradicated transmitting hereditary disease.
2 types of analysis possible
There are two different technologies available for DNA testing today :

Genetic results are a precious to help breeders to better predict the phenotype of the coming offspring
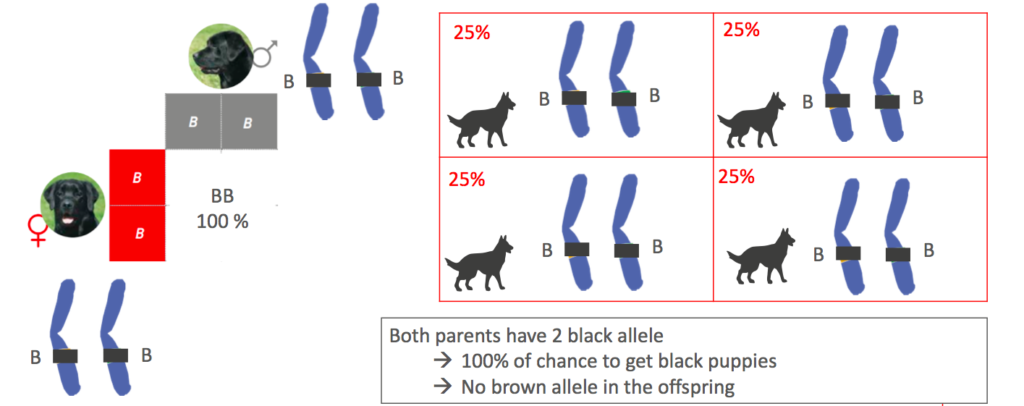
Example of DNA tasting and coat color :
mating 2 black labrador possibility 1
Example of DNA tasting and coat color :
mating 2 black labrador possibility 2
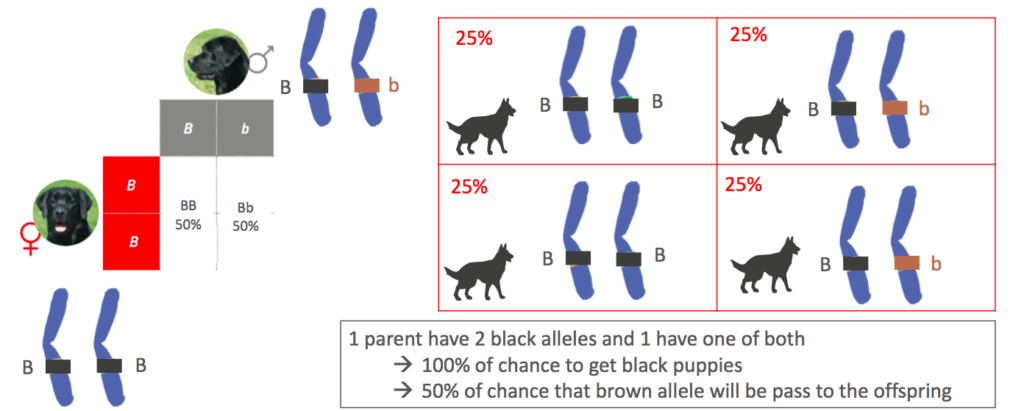
Example of DNA tasting and coat color :
mating 2 black labrador possibility 3
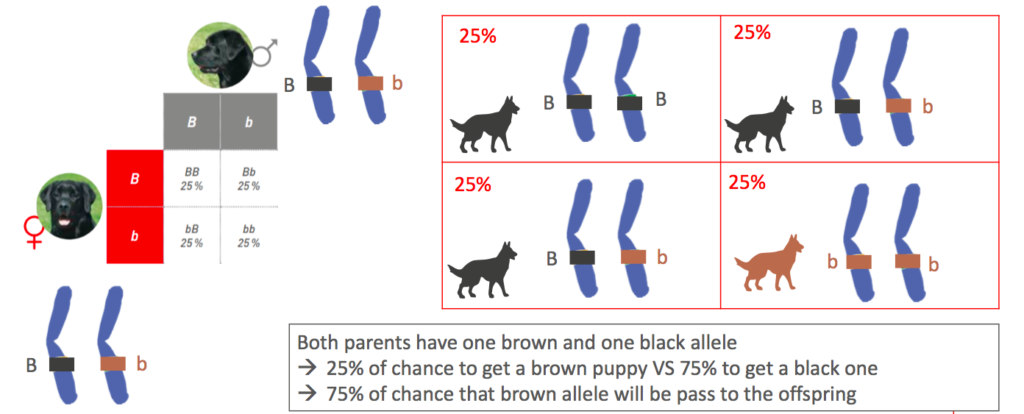
Example of DNA tasting and coat color

Genetic results are also a precious to help breeders to better control the genetic diseases transmission, while keeping genetic diversity inside their breeding
Example of mating risk for dominant disease
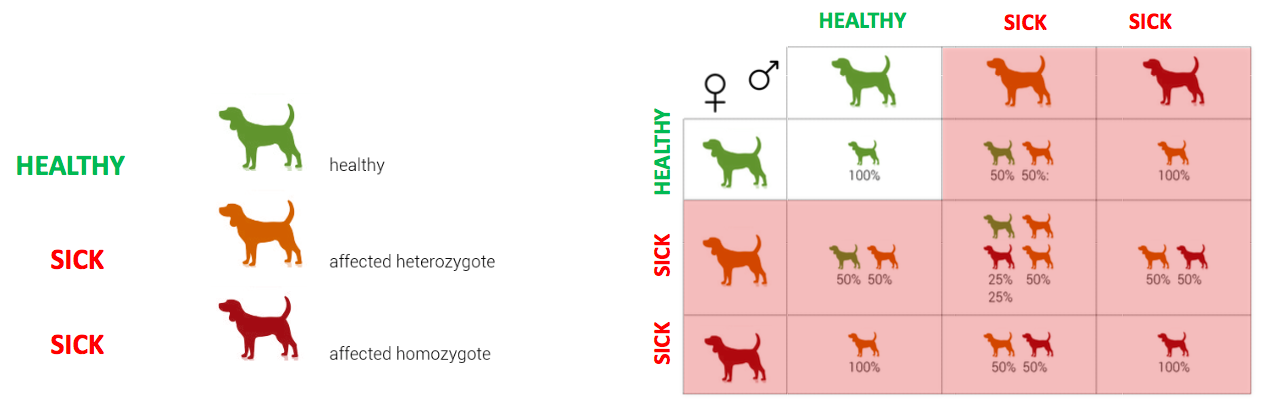
 Autosomal dominant inheritance : the dog needs 1 copie of the affected gene to express the disease
Autosomal dominant inheritance : the dog needs 1 copie of the affected gene to express the disease
Without DNA testing you can reproduce a dog that appear healthy but carry the disease gene :
- Passing of sick gene to puppies who will also be healthy carrier
- Two healthy carrier can produce sick puppies
Genetics and inbreeding
- Inbreeding : Inbreeding occurs when puppies are produced from two related dogs, i.e. dogs with relatives in common. High levels of inbreeding can affect the health of these puppies.
Using genetic test before mating dogs together is also useful to know their level of parentage and avoid reproducing too close relatives.
We do know that the higher the degree of inbreeding, the higher the risk is of the puppies developing both known and unknown inherited disorders. Inbreeding can also have an impact on the breed as a whole, e.g. reducing litter sizes and fertility.
Genetic testing to ensure the results of healthy and beautiful litters
Genetic test are useful to predict with certitude the appearance of the litters. When you are looking for a precise size or coat color it is a precise tool to measure for sure the probability of each phenotype. And it allows the breeder to select reproducers with the right knowledge of what each parent will bring to the litter.
And more than esthetic criteria it is also key to ensure a good health for the puppies. A responsible breeder will always try to reproduce to avoid genetic disease. But the only to do it with certitude is by genetically testing the dogs before mating.
Indeed, a dog can look healthy and carry a disease that is not expressed in his phenotype. Therefore, reproducing animals that looks healthy is not enough to ensure no transmission of hereditary disease.
INCLUDE GENETIC IN YOUR BREEDING
Demonstrate the benefits of using genetic testing such as MDD for breeders
Genetic and breed selection…
Selective breeding involves choosing parents with particular characteristics to breed together and produce offspring with more desirable characteristics.

And this is the key to working on dog breed selection.
Screening the parents’ genome will allow to better anticipate the mating result.
It’s an efficient tools to work on the genetic pool of breeding to give birth to beautiful healthy puppies.
MyDogDNA: A genetic test
developed by breed experts for breeders

What is the power of a genomic chip?
The array of cells makes it possible to carry out a very large number of genetic tests on a sample at one time.
Why include genetic in your breeding
Using genetics will allow you to better know your animals and therefore have all the informations needed to make the best mating in your breeding activity :
- Anticipating the apparence of the puppies and optimize your chances to have the desired featured (size, coat color, tails, …)
- Detecting possible genetic disease in healhty carrier to ensure giving birth of fully healhty puppies and avoid transmitting unwanted gene in the offspring
- Getting precious health info about your animal for potential risk of disease development in the future
- Providing scientific evidence on the good health of the puppies to the future pet owner that will come at their breeding to find their new life partner
Why include genetic in your breeding
Because genetic can be a complexe science and to help breeders get all the advantages of DNA test, the MyDogDNA report was especially made to help them understanding the results and how to apply them to their breeding program.
This is a very important point. Because you can have all the results that you want, but you need to have enough explanations to make this results actionable in a breeding plan. It was exactly our mindest when we thought about how to deliver the results to the breeder. How to make genetic simple and actionable.
That’s why we developed a dedicated report, with :
- On top of page the health conditions specific to the breed. With clear explanations on the disease, the first clinical signs, and the most important, what you can do with this result, I mean clear breeding advices to make conscious mating plan in your breeding.
- Then you also have others disease, and the traits.
A tailor-made report to support best breeding practices

All the results for each breed

GENETICS AND BREED STANDARDS
Explain how DNA testing can help in breed standards

